In an age where high-speed internet connectivity is not just a luxury but a necessity, fiber-optic technology has emerged as the backbone of modern telecommunications networks. Fiber-optic broadband offers unparalleled data transfer rates and reliability, making it the preferred choice for delivering high-bandwidth services to homes, businesses, and institutions.
Passive Optical Network (PON)
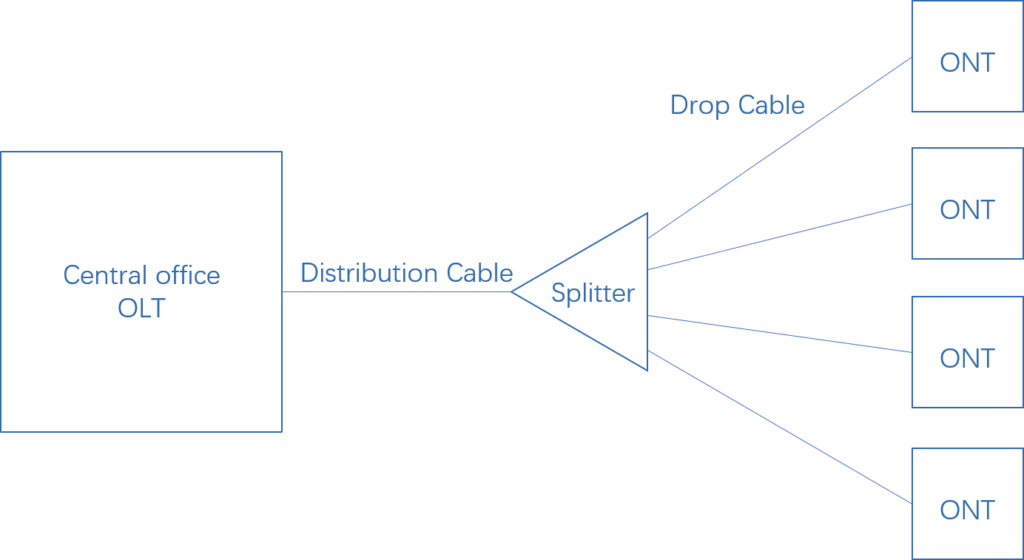
A Passive Optical Network (PON) is a network architecture that uses passive components to distribute optical signals to multiple subscribers. “Passive” implies that the PON does not require active electronic components. Instead, the network relies on passive splitters to divide the optical signal into multiple paths. This architecture allows for cost-effective and efficient broadband deployment over a wide area. There are two major PON standards currently, Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) and Ethernet Passive Optical Network (EPON). In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of each of these components and their role in the world of fiber-optic broadband.
Optical Line Terminal (OLT)
An Optical Line Terminal (OLT) is a crucial component in a PON system, which is the starting point of the Passive Optical Network (PON). The OLT serves as the central hub of the network, connecting the service provider’s core network to individual subscribers. It aggregates data from multiple ONUs or ONTs and manages the distribution of data traffic between them. OLTs are designed to handle high data rates and multiple protocols, ensuring efficient communication across the network. They also play a role in security and quality of service management.
Optical Network Unit (ONU)/Optical Network Terminal (ONT)
An Optical Network Unit (ONU) is a device used in a PON system to bridge the gap between the service provider’s infrastructure and the subscriber’s premises. ONUs are typically installed at the subscriber’s location, such as a home or business. They receive optical signals from the OLT and convert them into electrical signals that can be used by the subscriber’s devices, such as computers, phones, or routers. ONUs also transmit data generated by the subscriber’s devices back to the OLT.
The term Optical Network Terminal (ONT) is often used interchangeably with ONU with little subtle difference. ONT is a term used in ITU-T and ONU is a term used in IEEE, i.e. they refer to the same user side equipment in the PON system but are terms belonging to different standard bodies.
Optical Distribution Network (ODN)
The Optical Distribution Network (ODN) is the physical infrastructure that interconnects the various components of a PON system. It includes the fiber cables, optical splitters, connectors, and other passive components that facilitate the transmission of data between the OLT, ONUs or ONTs, and subscribers’ devices. ODNs are designed to minimize signal loss and ensure efficient distribution of data throughout the network.
The integration of Optical Line Terminals (OLTs), Optical Network Units (ONUs)/Optical Network Terminals (ONTs) and various optical components has revolutionized the way we experience high-speed broadband services. As the demand for faster and more reliable internet connectivity continues to grow, understanding these fundamental components becomes essential. With their combined capabilities, these components lay the foundation for a seamless and robust fiber-optic network that empowers individuals, businesses, and entire communities with cutting-edge communication possibilities.